
In the dynamic realm of startups, attracting and retaining top talent is crucial for survival and success. Traditional compensation packages often fall short in this competitive landscape. This is where equity-based incentives, like
etc come into play. These instruments offer employees a piece of the pie, aligning their interests with the company's growth and fostering a sense of ownership. To truly attract and retain top talent, startups must effectively utilize these tools. Stock options are strategically integrated into the CTC to attract and retain employees, particularly in the case of startups approaching IPOs. However, many job seekers accept these packages without fully comprehending their worth or considering the potential tax implications.
Firstly, we will discuss what ESOP and RSU are:
Employee stock options, also called share options, are a great way to reward employees. It's like giving them a special chance to buy a piece of the company they work for at a lower price. However, they must work for the company for a specific time to enjoy this special benefit.
The ESOP is a long-term employee benefit plan, designed to motivate and reward your employees. It allows you to provide your employees with a portion of ownership in the company. This is the best form of motivation for your employees because it provides them with a sense of ownership in the company. Your employees will work harder, and perform better. Because they know they have a stake in the company.
In Indian startups, ESOPs are a wonderful way for employers to bring in and keep talented people. They give employees a reason to stay with the company and become part-owners. This means employees can have more say in how things work.
RSUs are a type of restricted stock (which may also be known as letter stock or restricted securities). Restricted stock is company stock that cannot be fully transferable until certain restrictions have been met.
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) are like a special kind of work bonus where your company gives you shares in the company instead of extra cash. The catch is, these shares come with some rules. They're "restricted" because you can't just do whatever you want with them right away. There's a waiting period, called a vesting schedule, usually based on how long you've been working there. Sometimes, it's also tied to how well you're doing at your job. Your company might also have other rules about selling or transferring these shares, and they're all laid out in an agreement.
Now, RSUs are a bit different from Employee Stock Options (ESOP). With ESOP, you get the option to buy company shares in the future. But with RSUs, your company just gives you the shares upfront. Once that waiting period is over, these RSUs turn into regular company shares. You can vote on company matters, and you even get a piece of the company's profits through dividends.
Deciding on the number of shares you like to offer
As a startup founder, you need to decide on the number of shares you'd like to offer to the employee. This can be done by calculating the value at which each share will be sold and then dividing that number by the price per share of the company's stock. From there, we can determine how many shares you would like to offer.
Signing the startup stock option agreement
An employee is provided with a stock option agreement that delineates the rights of both the employee and employer concerning their stock options, encompassing any vesting conditions or expiration dates. Typically, an initial Offer Letter is extended to the employee, followed by a more comprehensive document or Plan Rules that require signatures from both parties. Total number of shares granted
Waiting for your stock to vest
Until stock options have vested, the holder cannot exercise them and, consequently, does not possess stockholder rights. This indicates that the option holder does not have complete entitlement to their portion until the options have vested. The vesting schedule serves the purpose of associating an obligation of performance or time with the options. This is why employee stock option plans prove to be a potent tool for motivating teams to remain with the company for an extended period and contribute more effectively to the company's ultimate success.
Exercising your options
Finally, when it comes time for your employees to exercise their options, they will do so through a brokerage account that is connected to your company's records. The proceeds from this sale are then split between the employee and the company based on whatever rate was agreed upon in the stock option agreement.
It's important to have an exit strategy in place so that everyone knows what will happen if the startup sells or goes public before all of the stock options are fully vested. It's also important for both parties (you and your employees) to understand their respective rights when it comes to selling, transferring, or exercising their options.
Taxation
When it comes to taxes, stock options can be taxed as either ordinary income or capital gains, depending on the type of option and how long it's held. Generally speaking, we will want to make sure that both parties understand any tax implications associated with the stock option agreement before signing off on it.
Overall, understanding how startup stock options work can help ensure that everyone involved is fully informed when making decisions about equity in your company.
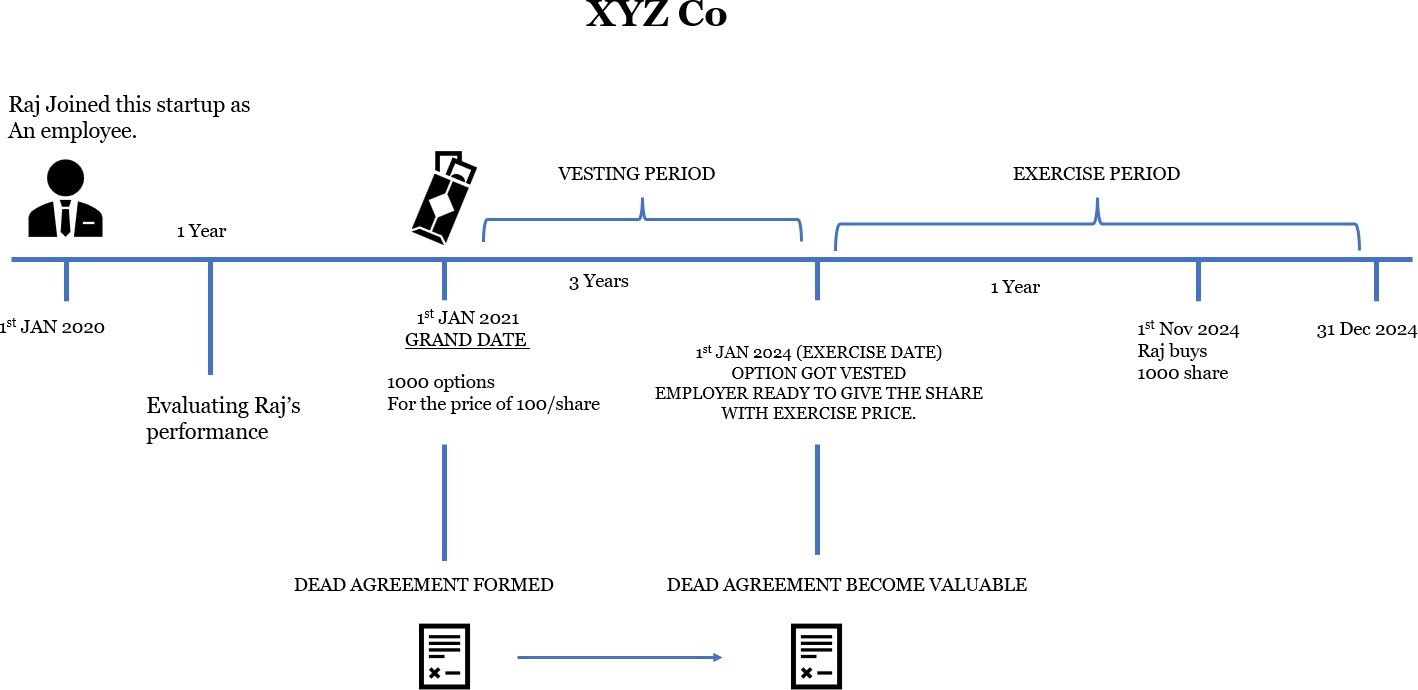
Establishing a Stock Option Plan during the initial phases of growth is highly recommended. This strategic move not only aids in attracting and retaining top talent but also serves as a powerful incentive for employees to align their focus with the company's long-term success. Moreover, implementing a stock option plan in the early stages proves advantageous for both founders, who benefit from enhanced talent attraction and retention, and employees, who secure a stake in the company at a lower exercise price. It's worth noting that although ESOPs persist in late-stage startups, early-stage employees enjoy the advantage of a lower exercise price. As the stock's fair market value increases, the elevated exercise price becomes progressively more costly for acquiring shares. When embarking on the journey of setting up. An ESOP, meticulous planning and legal guidance are imperative for all stakeholders— employees, advisors, founders, and investors alike. Founders should exercise prudence by establishing limits on the number of shares offered to prevent excessive dilution of existing shareholders.
The effectiveness of Stock options depends on how well they align with the company's culture, values, and goals. Regular communication, transparency, and a thoughtful approach to equity compensation are crucial for success in the startup ecosystem.
© 2026 Business Consultant & Law Firm - Legacy Partners. All Rights Reserved.
Designed by Nuewelle Digital Solutions LLP

Legacy Partners
We typically reply in a few minutes